1. What is an Air Compressor?
An air compressor is a machine that converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. It compresses and pressures atmospheric air, increasing the concentration of oxygen and other gases. The compressed air is then stored in a tank and can be used to power various types of tools and equipment, such as nail guns, spray paint guns, and air-powered impact wrenches.

The energy stored in the pressurized air can also be used to perform tasks such as inflating tires, powering pneumatic machinery, and operating various industrial machinery. Air compressors come in a variety of sizes and configurations, including portable models for home use, and larger industrial models for commercial and industrial applications.
2. Types of Air Compressors
①. Piston Air Compressors
Piston compressors work by using a piston to compress air and store it in a tank. The basic operation of a piston compressor involves the following steps:
A. Suction: The piston moves down, creating a vacuum in the cylinder that draws in air from the outside.
B. Compression: The piston moves back up, compressing the air in the cylinder. The amount of compression depends on the size of the cylinder, the length of the stroke, and the number of pistons.
C. Discharge: The compressed air is then expelled from the cylinder and into the storage tank.
D. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled and the moisture is removed from it to prevent corrosion in the storage tank and pipes.
E. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.

Features and Applications
Piston compressors are available in single-stage and two-stage models. Single-stage models compress air in one pass, while two-stage models compress air in two passes, resulting in higher pressure and more efficient operation.
Piston compressors are often used in various applications, including powering air tools, inflating tires, and operating pneumatic machinery. They are available in a range of sizes, from small portable models for home use to large industrial models for commercial and industrial applications.
②. Rotary Screw Air Compressors
Rotary screw compressors work by using two rotors to compress air, which is then stored in a tank. The basic operation of a rotary screw compressor involves the following steps:
A. Intake: Air is drawn into the compressor through an inlet filter and into the compression chamber between the rotors.
B. Compression: The rotors, which are specially shaped screws, rotate and move the air through the compression chamber, compressing it to the desired pressure.
C. Discharge: The compressed air is expelled from the compression chamber and into the storage tank.
D. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled to remove the heat generated during the compression process and to prevent condensation in the storage tank and pipes.
E. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.

Applications and features
Rotary screw compressors are often used in industrial and commercial applications because they can produce a large volume of compressed air continuously. They are available in a range of sizes, from small portable models for on-the-go applications to large industrial models for use in manufacturing facilities and other commercial settings.
The rotary screw design allows for smooth, continuous operation and low noise levels, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications. The ability to adjust the output pressure of rotary screw compressors also makes them a versatile option for many industries and applications.
③. Centrifugal Air Compressors
Centrifugal air compressors work by using a spinning impeller to compress air and increase its pressure. The basic operation of a centrifugal compressor involves the following steps:
A. Intake: Air is drawn into the compressor through an inlet filter and into the eye of the impeller.
B. Acceleration: The impeller, which is a spinning wheel with radial blades, accelerates the air and moves it outwards towards the rim of the impeller.
C. Compression: As the air moves towards the rim of the impeller, it is compressed by the centrifugal force generated by the spinning impeller. The compressed air is then expelled from the impeller and into the discharge pipe.
D. Discharge: The compressed air is expelled from the discharge pipe and into the storage tank.
E. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled to remove the heat generated during the compression process and to prevent condensation in the storage tank and pipes.
F. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.
Features and applications
Centrifugal compressors are often used in high-volume, high-pressure applications, such as power generation and petroleum refining. They are also commonly used in air separation plants to produce nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases.
The high-speed operation of centrifugal compressors allows for efficient compression and the ability to handle large volumes of air, making them a popular choice for industrial and commercial applications where high-volume compressed air is required. The design also allows for low noise levels, making it a suitable option for applications where noise levels are a concern.
④ Scroll Air Compressors
Scroll compressors, also known as spiral compressors, work by using two spiraling scrolls to compress air. The basic operation of a scroll compressor involves the following steps:
A. Intake: Air is drawn into the compressor through an inlet filter and into the center of the compression chamber, where the two spiraling scrolls are located.
B. Compression: The two spiraling scrolls, one fixed and one orbiting work together to compress the air. As the orbiting scroll orbits around the fixed scroll, it pushes the air toward the outer circumference of the compression chamber. The air is then trapped between the two scrolls and compressed as the volume of the trapped air decreases.
C. Discharge: The compressed air is expelled from the compression chamber and into the storage tank.
D. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled to remove the heat generated during the compression process and to prevent condensation in the storage tank and pipes.
E. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.
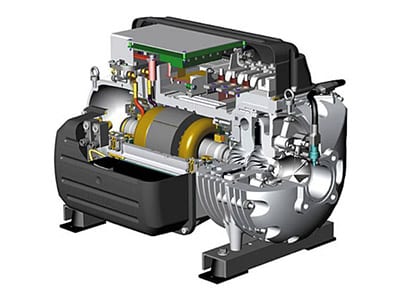
Features and applications
Scroll compressors are often used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, as well as in smaller industrial and commercial applications where quiet, low-maintenance operation is required. They are also commonly used in portable air compressors and other applications where space is limited.
The simple and compact design of scroll compressors allows for efficient and reliable operation, as well as low noise levels. The lack of reciprocating parts also means that scroll compressors are generally low maintenance, making them a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
⑤ Diaphragm Air Compressors
Diaphragm compressors, also known as membrane compressors, work by using a flexible diaphragm to compress air. The basic operation of a diaphragm compressor involves the following steps:
A. Intake: Air is drawn into the compressor through an inlet filter and into the compression chamber, which is divided into two compartments by the diaphragm.
B. Compression: A pulsing mechanism, such as a piston or an eccentric drive, is used to move the diaphragm back and forth, compressing the air in one compartment and creating a vacuum in the other. As the diaphragm compresses the air, it increases its pressure.
C. Discharge: The compressed air is expelled from the compression chamber and into the storage tank.
D. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled to remove the heat generated during the compression process and to prevent condensation in the storage tank and pipes.
E. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.

Diaphragm compressors are often used in applications where air purity is a concern, such as food and beverage processing and pharmaceuticals. They are also commonly used in pneumatic systems and other applications where oil-free compressed air is required.
The simple and oil-free design of diaphragm compressors allows for clean and efficient operation, making them a popular choice for applications where air purity is a concern. They are also relatively quiet and low maintenance, making them a suitable option for a wide range of applications.
⑥ Portable Compressors
Portable air compressors are designed to be easily moved and used in a variety of locations. They typically use either a piston or a rotary screw compressor to compress air, and the basic operation of a portable compressor involves the following steps:
A. Intake: Air is drawn into the compressor through an inlet filter and into the compression chamber.
B. Compression: Depending on the type of compressor used, the air is compressed either by a piston moving back and forth in a cylinder or by a rotating screw that compresses the air.
C. Discharge: The compressed air is expelled from the compression chamber and into the storage tank.
D. Cooling: After discharge, the compressed air is cooled to remove the heat generated during the compression process and to prevent condensation in the storage tank and pipes.
E. Storage: The compressed air is stored in the tank, ready to be used when needed.
F. Delivery: The compressed air is delivered to the tool or device being used through a hose and air regulator.
Applications and features
Portable air compressors are commonly used for various applications, including powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, and running air-powered equipment. They are designed to be portable and convenient and are often used in construction sites, workshops, and other locations where a source of compressed air is needed.
The compact size and portability of portable air compressors make them a popular choice for a wide range of applications. They are generally easy to use and low maintenance, and are available in a variety of sizes and configurations to meet the needs of different users.
Get Ingersoll Rand and Atlas Air Compressors at the Lowest Price
If you are looking for Ingersoll Rand and Atlas Copco products at good prices then please do not hesitate to contact us, YScompressor, the trusted Chinese factory of Ingersoll Rand and Atlas air compressors. We offer original products at competitive prices, and we are always here to assist you with your air compression needs.